 |
This project uses L298 (known as H-bridge) to run brushless motor (taken from HDD) via Arduino Pro Mini. By this project, we also know how brushless works
1. PCB H-bridge L298 (2pcs)
2. Arduino Pro Mini
3. Brushless motor (take from HDD)
 |
| 1. H-Bridge L298 |
 |
| 2. Arduino Pro Mini |
1. Understand brushless motor principle
 |
| Image of brushless motor of HDD |
Motor stator will make magnetic field -> when magnetic direction moving -> it will move rotor
Let's see how magnetic field moving:
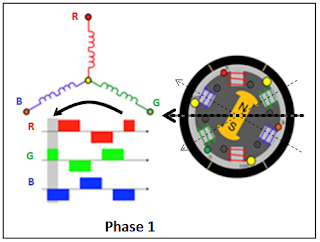
Stator of motor has 3 wire, connected together at 1 point, other point of wire will connect to power source.
At "phase 1", power (+) is applied to Green coil, and power (-) is applied to Blue coil -> sum of vector magnetic field of Green coil and Blue coil will make magnetic direction as in above picture (horizontal direction) -> this magnetic field will make rotor rotating and align to magnetic direction, then stop at this direction
To move rotor, magnetic field must moving -> see "phase 2"
In "phase 2", power (+) is applied to Red coil, and power (-) is applied to Blue coil -> sum of vector magnetic field will make magnetic direction as in above picture -> this magnetic field will move rotor to this direction
Continue with phase 3, 4, 5, 6 -> magnetic field rotates 1 circle -> rotor also rotates 1 circle
2. Driver for brushless motor
A Driver for brushless motor is used to arrange power (+) and power (-) synchronizing to each coil Blue, Red, Green for rotating magnetic field
Following table is summarize of power (+) and power (-) need to apply each coil at each phase:
Phase
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
Blue
|
-
|
-
|
N
|
+
|
+
|
N
|
Red
|
N
|
+
|
+
|
N
|
-
|
-
|
Green
|
+
|
N
|
-
|
-
|
N
|
+
|
3. Connection to L298 H-bridge
Half of H-bridge is used to connect to each coil of brushless motor
Look inside L298 IC -> it is possible to flow current from half H-bridge to another half H-bridge
4. Circuit connection
Schematic diagram by Fritzing:
ENA IN1 is connected to H-bridge 1
ENB IN3 is connected to H-bridge 2
ENC IN1 is connected to H-bridge 3
This project need 3 half of H-bridge -> need 2 L298 PCB. Here is my result connection:
 |
| Result of connection |
For this connection, we have pattern code as here:
Phase
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
Blue
|
-
|
-
|
N
|
+
|
+
|
N
|
Red
|
N
|
+
|
+
|
N
|
-
|
-
|
Green
|
+
|
N
|
-
|
-
|
N
|
+
|
ENA
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
IN1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
ENB
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
IN3
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
ENC
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
IN1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
5. Coding for Arduino
/* Motor - brushless motor control Created 07 Jan. 2018 This example code is in the public domain. http://engineer2you.blogspot.com */ const byte en_A = 2; const byte in_A = 3; const byte en_B = 4; const byte in_B = 5; const byte en_C = 7; const byte in_C = 8; int speed_motor = 20; void setup() { pinMode(en_A,OUTPUT); pinMode(in_A,OUTPUT); pinMode(en_B,OUTPUT); pinMode(in_B,OUTPUT); pinMode(en_C,OUTPUT); pinMode(in_C,OUTPUT); // start serial port at 9600 bps: Serial.begin(9600); while (!Serial) { ; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only } } void loop() { //increasing speed gradually by loop for (int i = 0; i<=(21-speed_motor)*5; i++) { motor_run(); } if (speed_motor > 2) speed_motor = speed_motor - 1; //increasing speed Serial.println(speed_motor); //print out speed to serial port } void motor_run() { digitalWrite(en_A,1); digitalWrite(in_A,0); digitalWrite(en_B,0); digitalWrite(in_B,0); digitalWrite(en_C,1); digitalWrite(in_C,1); delay(speed_motor); //Phase 1 digitalWrite(en_A,1); digitalWrite(in_A,0); digitalWrite(en_B,1); digitalWrite(in_B,1); digitalWrite(en_C,0); digitalWrite(in_C,0); delay(speed_motor); //Phase 2 digitalWrite(en_A,0); digitalWrite(in_A,0); digitalWrite(en_B,1); digitalWrite(in_B,1); digitalWrite(en_C,1); digitalWrite(in_C,0); delay(speed_motor); //Phase 3 digitalWrite(en_A,1); digitalWrite(in_A,1); digitalWrite(en_B,0); digitalWrite(in_B,0); digitalWrite(en_C,1); digitalWrite(in_C,0); delay(speed_motor); //Phase 4 digitalWrite(en_A,1); digitalWrite(in_A,1); digitalWrite(en_B,1); digitalWrite(in_B,0); digitalWrite(en_C,0); digitalWrite(in_C,0); delay(speed_motor); //Phase 5 digitalWrite(en_A,0); digitalWrite(in_A,0); digitalWrite(en_B,1); digitalWrite(in_B,0); digitalWrite(en_C,1); digitalWrite(in_C,1); delay(speed_motor); //Phase 6 }










0 Comments: